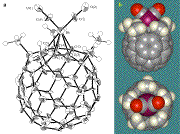
(1) Synthesis of transition metal-fullerene complex
(2) Theoretical studies on organocuprate reaction mechanism
(3) Creation of new organic functional molecules by way of fullerene functionalization
(1) Synthesis of transition metal-fullerene complex
Chemically modified fullerenes have attracted much interest owing to their potential applicability as functional molecules having unique chemical and physical properties. We have focused on the hybridization of the fullerene with transition metal fragments to create new catalysts and material. We successfully synthesized the rhodium complexes bearing penta-methylated [60]fullerene, Rh(h5-C60Me5)(CO)2. Electrochemical properties and catalytic activities of hydrosilylation of the new molecule were investigated. These results indicated that transition metal-fullerene complex has an extended dp-pp conjugate system among the metal center, the cyclopentadienide on a pole, and the residual C50/50-p electron system.

J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 12407-12408 (2000).
Org. Lett. 2, 1919-1921 (2000).
(2) Theoretical studies on organocuprate reaction mechanism
We have focused on the organocopper reactions, which have been recognized as one of the most important synthetic reactions in organic chemistry. Recent development in computational chemistry now allows us to understand the complicated molecular events in reaction flasks. With the aid of large scale quantum mechanical calculations, we have shown the importance of the cooperative effects of polymetallic clusters in carbocupration and conjugate addition reactions. The same principle was found to be applicable to the other representative organocopper reaction, such as SN2 reaction with haloalkanes and epoxides. Based on the polymetallic cluster mechanism, acceleration effect of the Lewis acidic additives, such as BF3, was explained for the first time. These studies give not only a mechanistic insight but also a guiding principle to design the reactions.
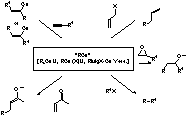
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 1826-1827 (2000).
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 7294-7307 (2000).
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 3750-3771 (2000).
(3) Creation of new organic functional molecules by way of fullerene functionalization
Based on the development of new synthetic methods of organofullerenes, we have aimed at the design and synthesis of functional molecules. We focused on the development of functional molecules that target important biomolecules and created a new DNA binding fullerene. After searching biological functions, we found that the DNA binding fullerene can deliver excellular DNA into mammalian cells and induce expression of its foreign genes. Gene delivery is one of the important techniques for development of the gene therapy.
Å@
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 4254-4257 (2000)
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 4257-4259 (2000)