(1) New aspect of olefin carbometalation
(2) Mechanistic studies on organocopper reactions
(3) Creation of new organic functional molecules by way of fullerene functionalization
(1) New aspect of olefin carbometalation
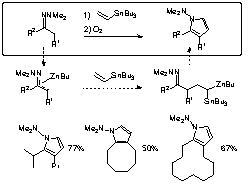
We have focused on the addition of organometallics to an olefin, which will develop a new paradigm for organic synthesis. We reported that the use of a zincated hydrazone of a ketone realizes the efficient addition of the metal enolate equivalent to ethylene. Recently we found the addition of the zincated hydrazone to vinyl stannane also proceeds to generate a Zn/Sn dimetallic species having electrophilic and nucleophilic centers in the same molecule. This novel carbometalation product can be converted to pyrrole derivatives upon exposure to molecular oxygen. Construction of pyrrole ring structure, which is found frequently in biologically active compounds, was thus achieved in one-pot from hydrazone and olefinic substrate under mild conditions.

Org. Lett. 1, 1505-1507 (1999).
(2) Mechanistic studies on organocopper reactions
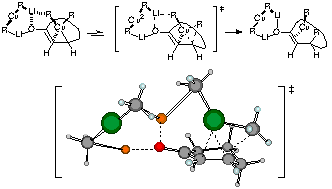
Although organocoppers have been recognized as one of the most important class of organometallic reagent, the mechanisms of the reactions have been rather obscure. We have studied those reaction mechanisms with the aid of large scale molecular orbital calculations, and proposed the importance of the cooperative effects of polymetallic clusters. The large scale computation on the addition of lithium organocuprate to cyclohexenone revealed that the reductive elimination of Cu(III) intermediate, which consists of an open cuprate cluster and cyclohexenone, is the crucial face-selection step of the olefin as well as the rate-determining step of the reaction. The structures of the polymetallic intermediates and transition states not only account for various experimental facts but provide guide lines for further design of useful reactions including asymmetric reactions.
Chem. Eur. J., 5, 1534-1543 (1999).
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 121, 8941-8942 (1999).
(3) Creation of new organic functional molecules by way of fullerene functionalization
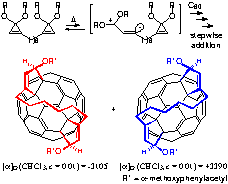
We found that a reaction between [60]fyllerene and vinylcarbene species, which is generated from bis cyclopropenone acetal precursor, gives organofullerenes in good yield. Reigoselectivity of the second addition of the vinyl carbene is controlled by the hexamethylene tether to give C2 chiral organofullerene predominantly. Resolution of the racemic mixture by using MTP acid afforded enantiomerically pure compounds. These chiral fullerens are unique and expected to be a new structural motif in biochemical and material science.
Å@
Fullerene Science & Technology, 7, 519-528 (1999).